Despite having only two additional installed software under CentOS 7 it is not a good idea to just try upgrading only CentOS 7 to CentOS Stream 9. There is no clear and supported path for upgrading from CentOS 7 to CentOS Stream 9 and even to the older one CentOS 8 (or CentOS Stream 8). The best way is to just make a clean install of CentOS Stream 9 and copy all the Elasticsearch and Kibana files and this article is how to do it without problems.
Here is the plan to move the existing installation of Elasticsearch and Kibana services from CentOS 7 to CentOS Stream 9:
- Make a clean install of CentOS Stream 9
- Update the current Elasticsearch and Kibana installations to their last versions (from their branch or minor versions).
- Add Elasticsearch and Kibana repositories to the new system. Tune the system crypto policies.
- Install Elasticsearch and Kibana software packages, but do not start the services.
- Copy Elasticsearch and Kibana important files such as the index directory and the configuration directories. Check the user and group IDs of the files.
- Start the Elasticsearch and Kibana services.
In this example, the installation of the new server is just starting a new LXC container, which will host the Elasticsearch and Kibana services. There is no difference between using a container or a physical machine. With LXC container it is easier to copy the needed files such as the Elasticsearch index files, which may be tens of terabytes or more, and various configuration files.
STEP 1) Make a clean install of CentOS Stream 9
Check out the following article on the purpose – Network installation of CentOS Stream 9 (20220606.0) – minimal server installation or if LXC container is preferred – Run LXC CentOS Stream 9 container with bridged network under CentOS Stream 9.
Creating a LXC container of CentOS Stream 9 is really simple and fast:
[root@srv ~]# lxc-create --template download -n kibana.u1x2.com -- --dist centos --release 9-Stream --arch amd64 The cached copy has expired, re-downloading... Downloading the image index Downloading the rootfs Downloading the metadata The image cache is now ready Unpacking the rootfs --- You just created a Centos 9-Stream x86_64 (20230511_19:27) container.
Then tune the network following the above article. It is a good idea when configuring the network to preserve the original UUIDs and network addresses (MAC address, too) of the LXC containers network and the inner container’s interface.
So copy the UUID from /var/lib/lxc/loganalyzer-old/rootfs/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 to the CentOS Stream 9 network configuration – /var/lib/lxc/loganalyzer/rootfs/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/ethernet-eth0.nmconnection, which uses NetworkManager. And the LXC container’s MAC address: the variable lxc.net.0.hwaddr from /var/lib/lxc/loganalyzer/config to /var/lib/lxc/loganalyzer/config.
The last step is to run the newly installed system. No errors in the output signals for a successful start-up of the LXC container with the name loganalyzer.
[root@srv ~]# lxc-start -n loganalyzer [root@srv ~]#
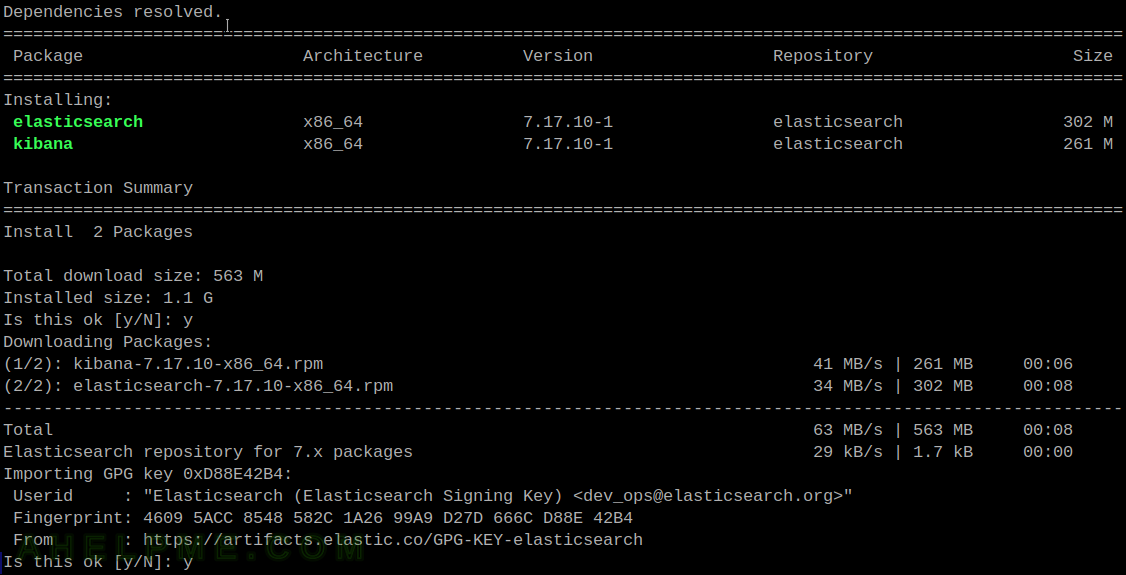
STEP 2) Upgrade the current Elasticsearch and Kibana installations to their last versions (from their branch or minor versions).
For example, if the current Elasticsearch is version 7. It is good to upgrade it to the latest version from 7.x before proceeding with the next steps.
The current installed versions of Elasticsearch and Kibana software are from the branch 7 – 7.17.4-1 and the latest version is 7.17.10-1.
Check in the old system with (CentOS 7):
[root@loganalyzer-old ~]# yum list installed|egrep -e "(elasticsearch|kibana)" elasticsearch.x86_64 7.17.4-1 @elasticsearch kibana.x86_64 7.17.4-1 @elasticsearch