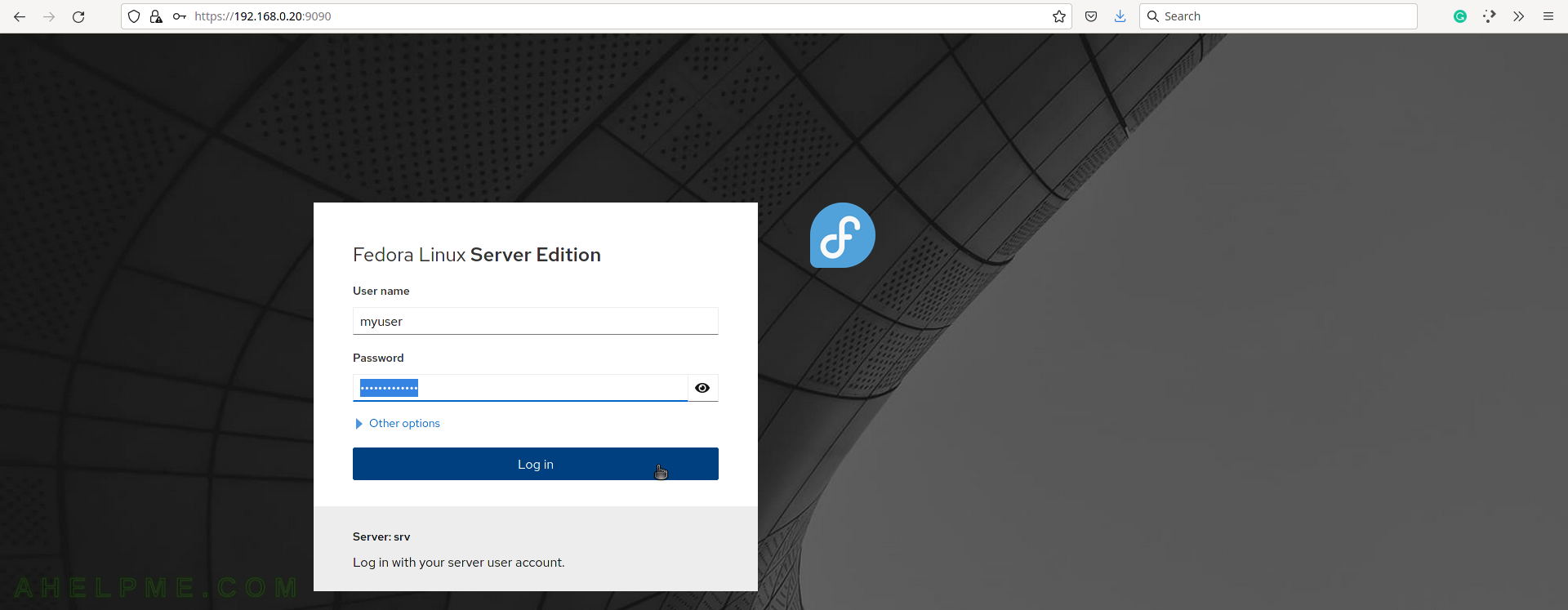
SCREENSHOT 1) The cockpit login page.
Use an administrative user to log in successfully. If the root is not permitted to remote log in using SSH, the root user could not log in.
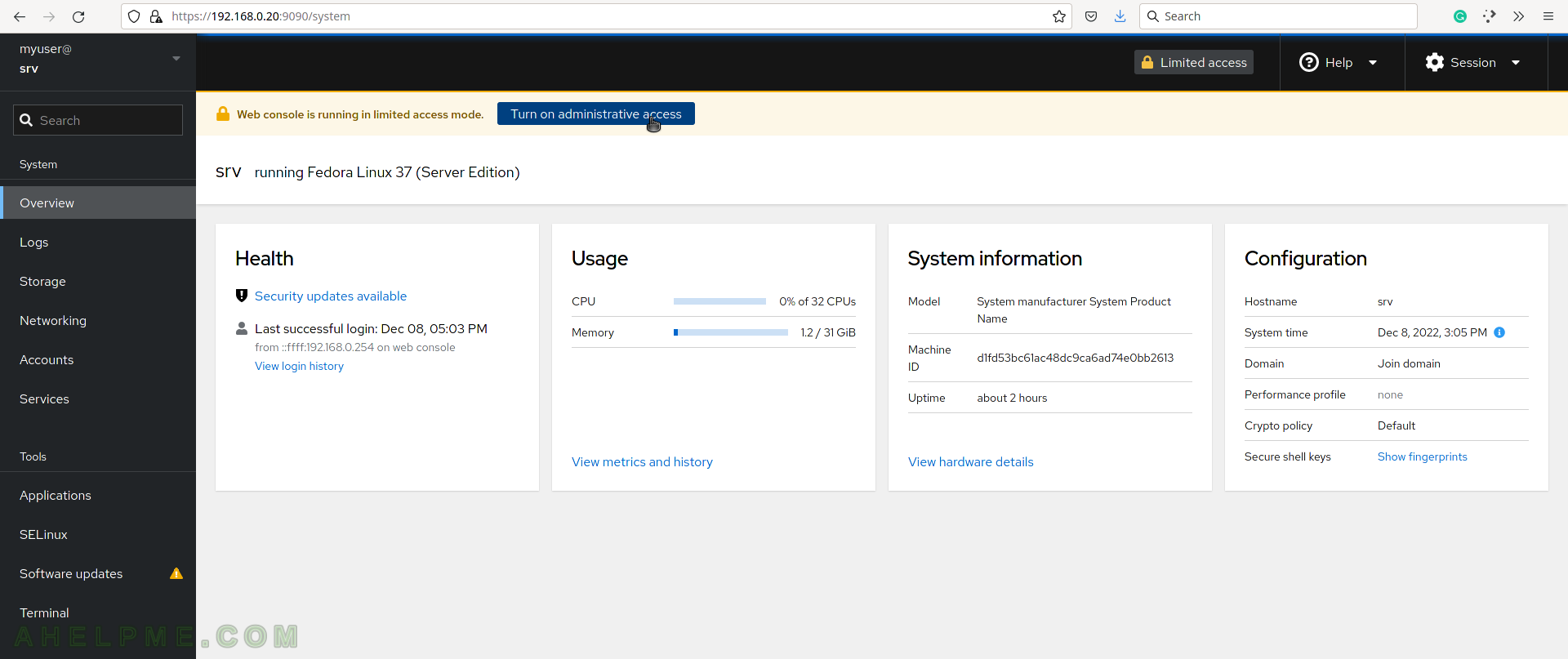
SCREENSHOT 2) The web console is running in limited access mode.
To enable administrative access click on “Turn on administrative access”.
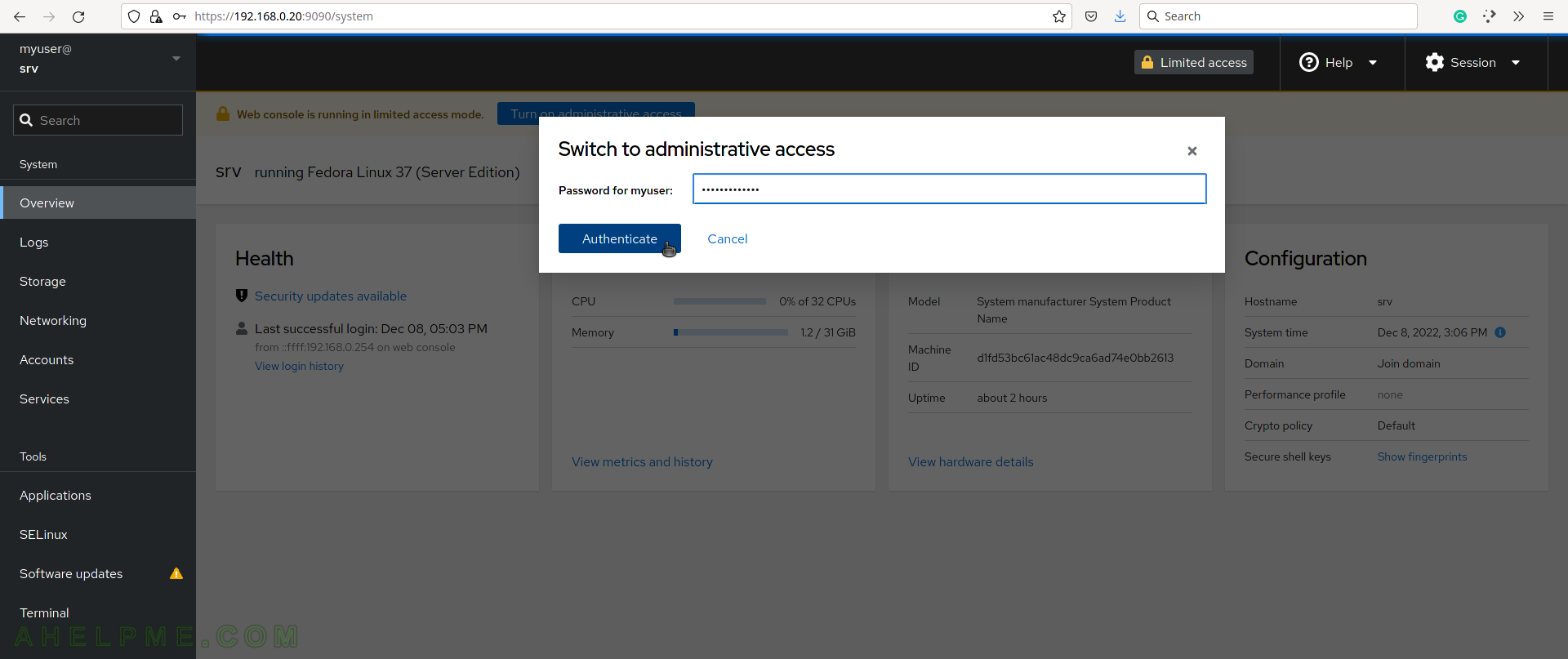
SCREENSHOT 3) Enter the user password to enable administrative access. The logged user must have administrative privileges.
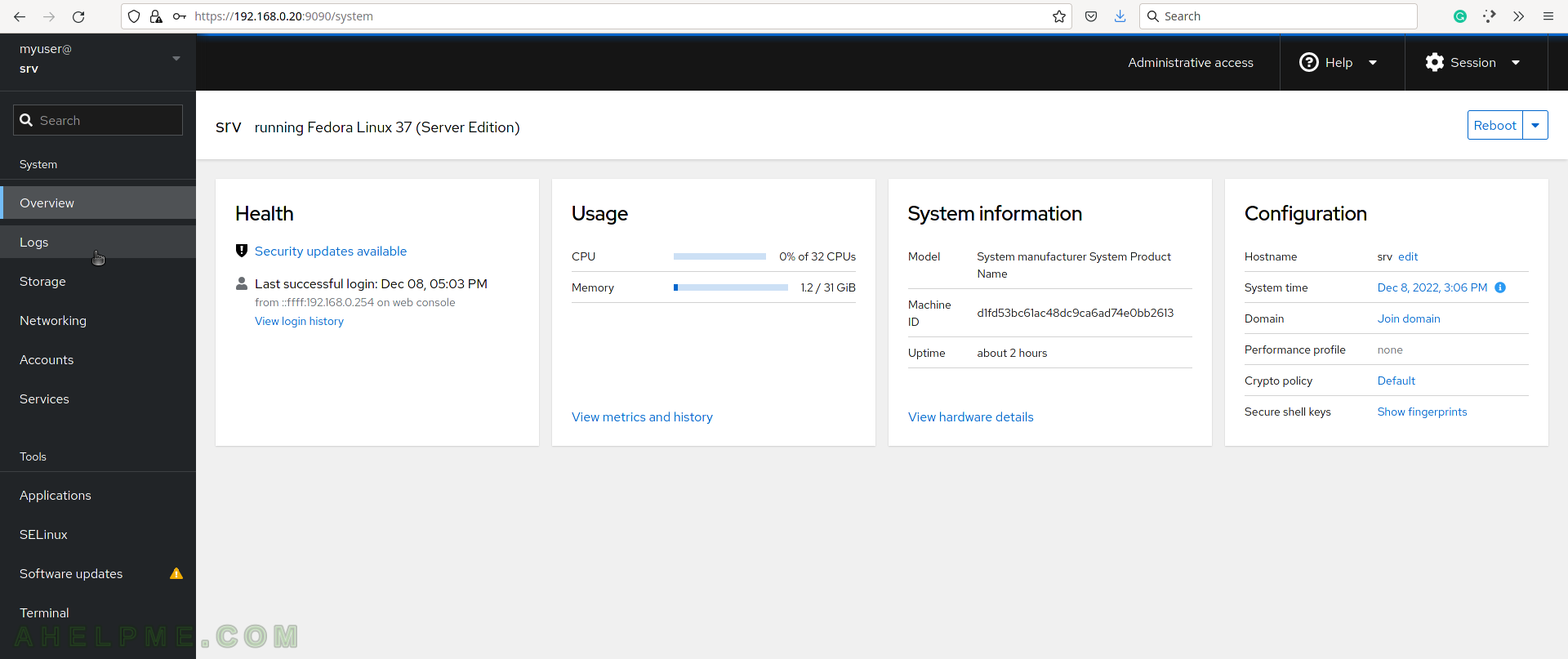
SCREENSHOT 4) After successful login, the System overview screen is shown.
It resembles a dashboard with brief information about the system’s Health, Usage, System Information, and Configuration.
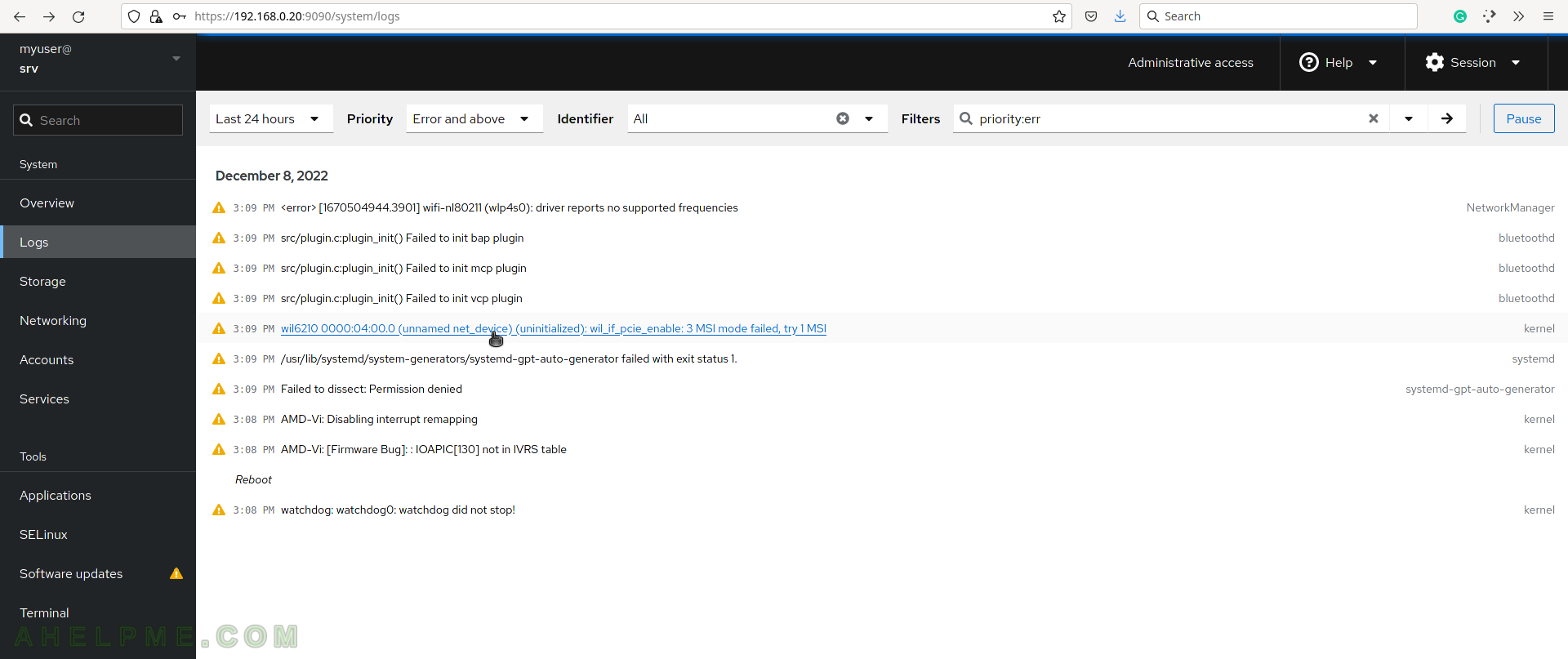
SCREENSHOT 5) The logs page shows the last 24 hours’ logs with priority “error”.
There are multiple filters – Hours, Priority, Identifier, and editable filter fields.
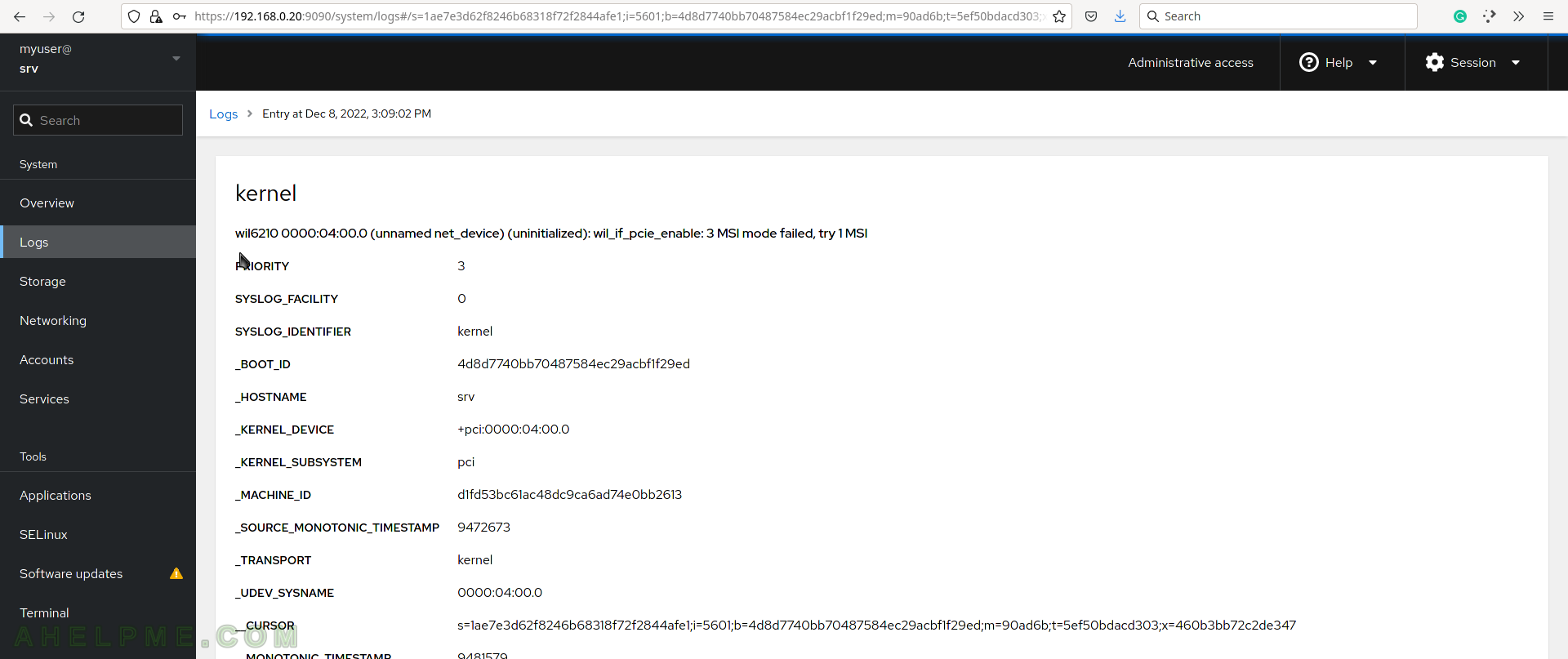
SCREENSHOT 6) Clicking on a log entry will display a detailed page for the error.
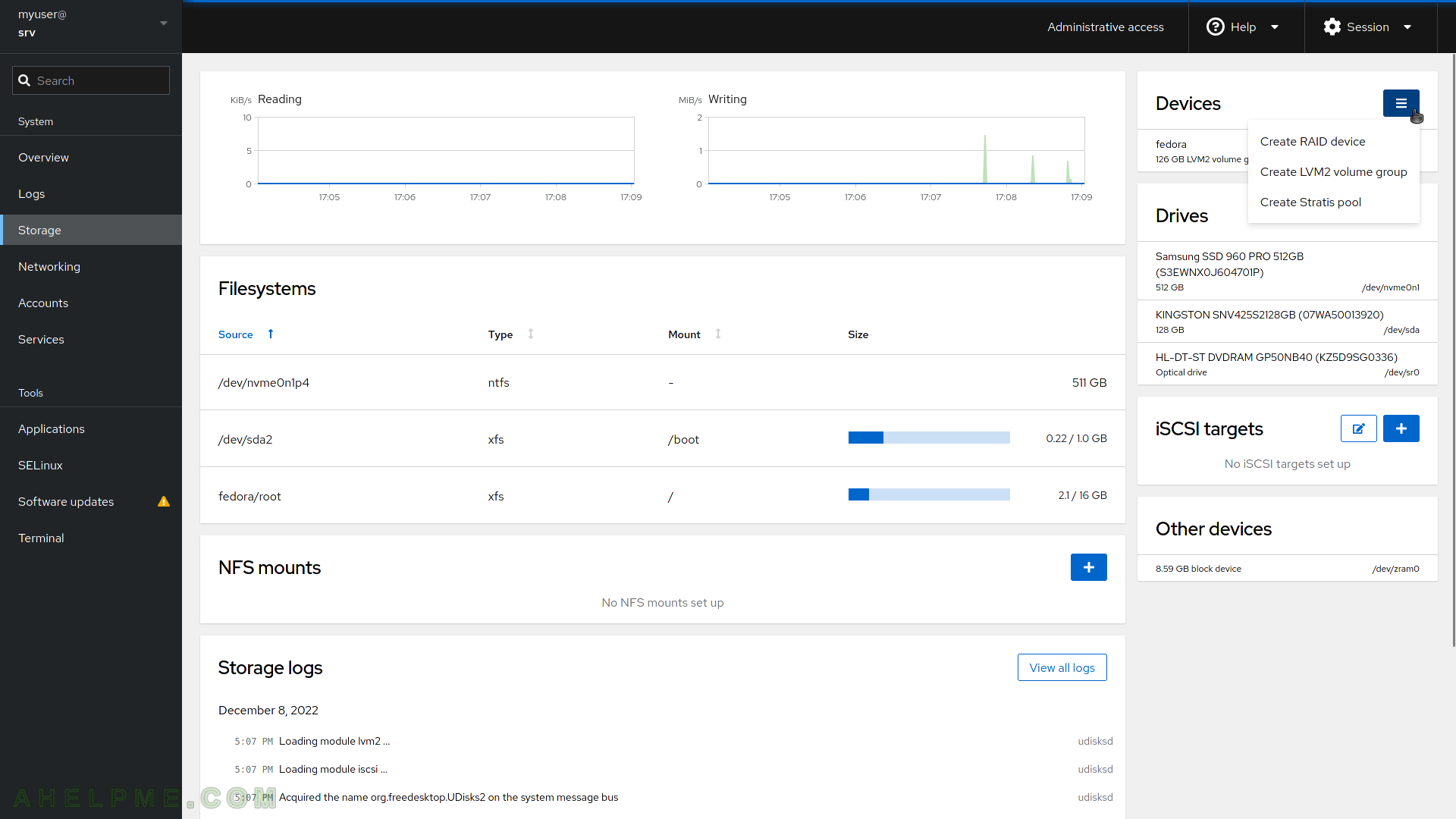
SCREENSHOT 7) The Storage page shows real time read and write statistics, information for the filesystems, drives, devices (there is a RAID functionality), iSCSI targets, and NFS mounts and functionality to add and manage ones. In addition, there are Storage logs at the bottom of the page.
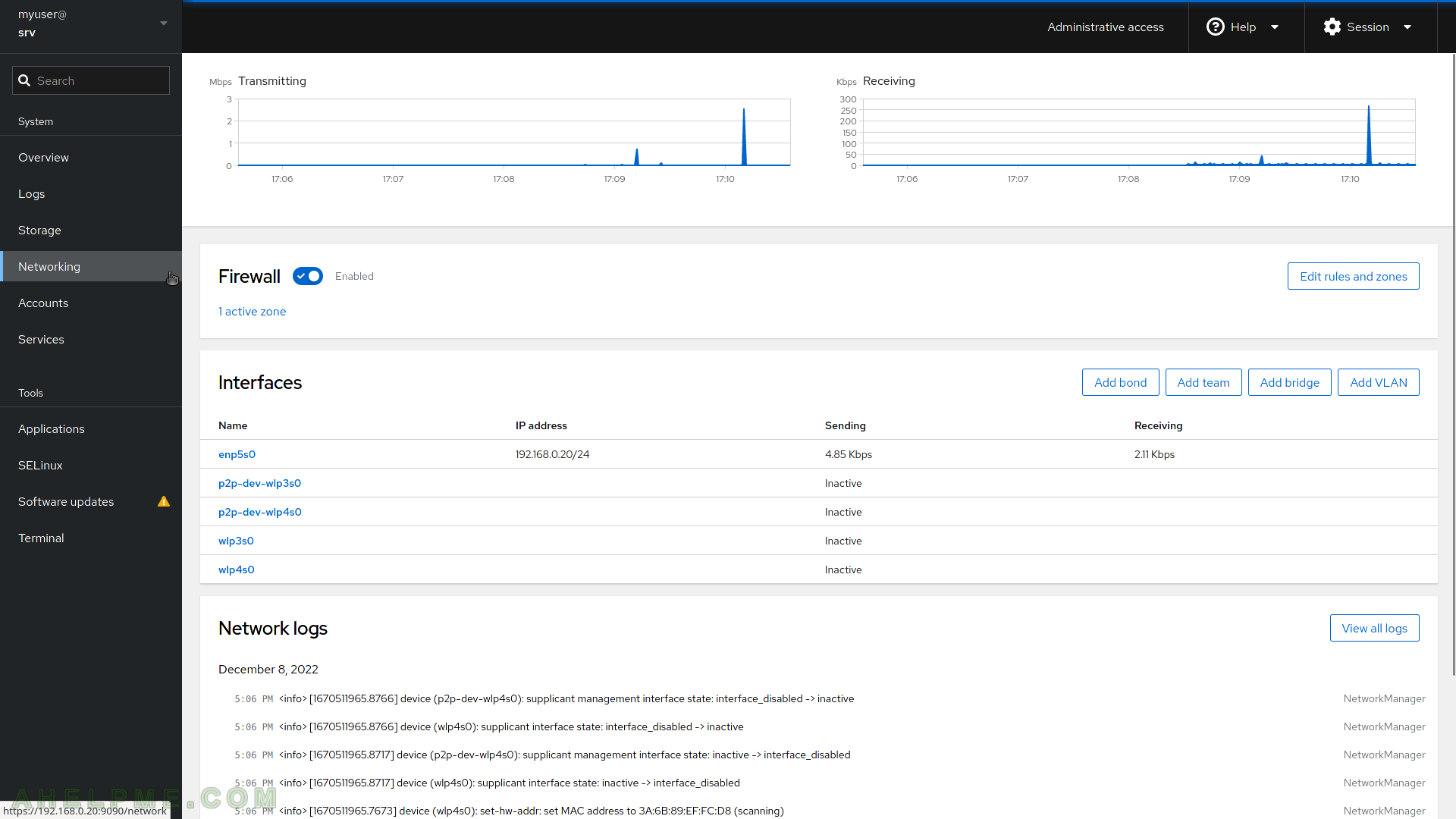
SCREENSHOT 8) The Networking page includes information for real-time Transmitting and Receiving bandwidth.
Firewall rules, which can be added or deleted. All interfaces and the current IP and bandwidth and at the bottom, there are the last records of the Network logs. Networking configurations such as IPv4, IPv6, DNS, MTU, and MAC could be modified.
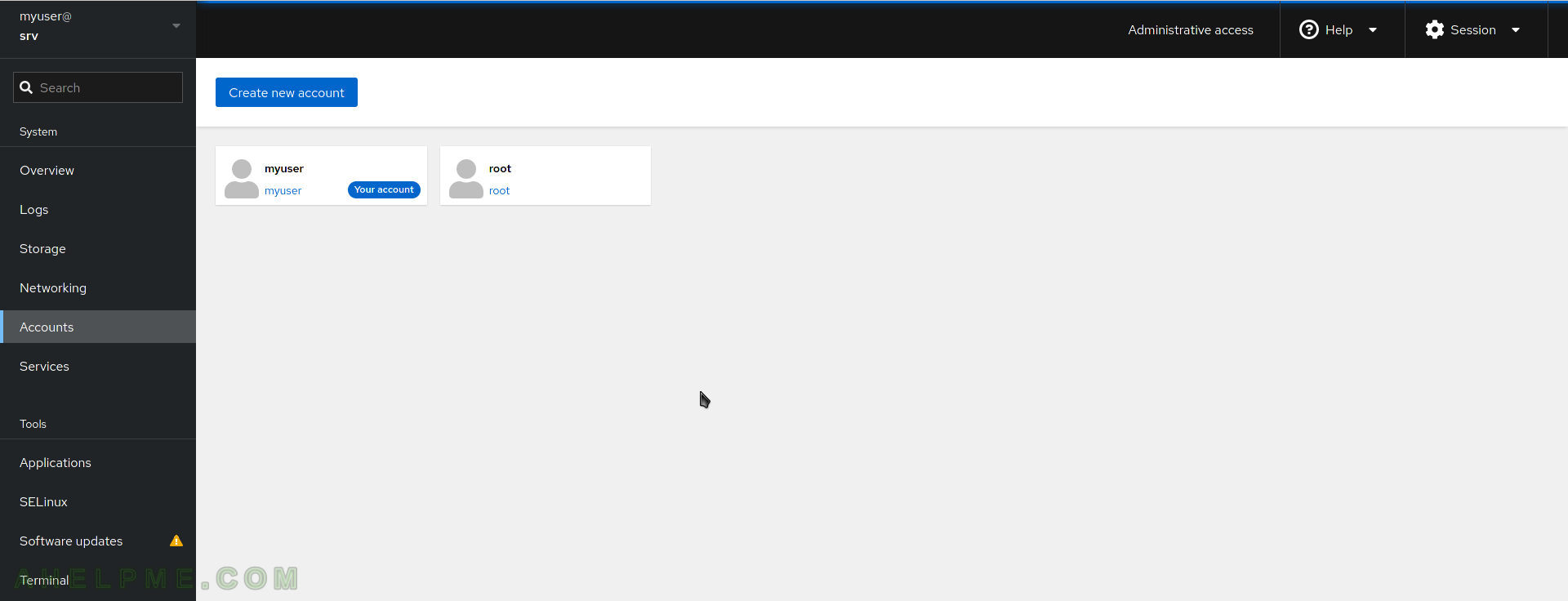
SCREENSHOT 9) All user accounts and simple management such as create, update, delete, and Login history.
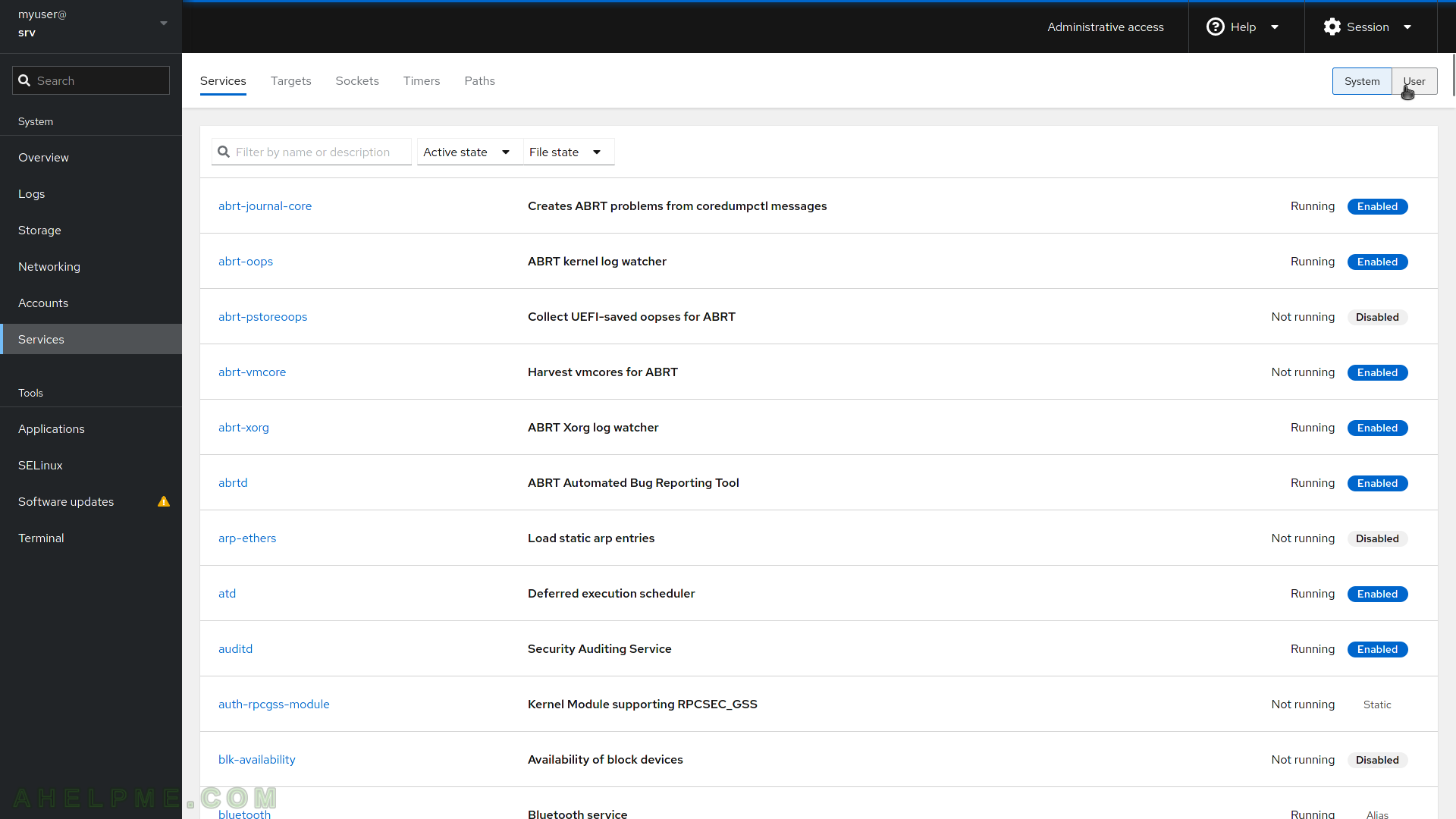
SCREENSHOT 10) Services pages offer management of the systemd services, targets, sockets, timers, and paths.
For each service it is included relationships, path, memory, and the last logs.
SCREENSHOT 11) To show all applications check if there are new ones with the top left button for a refresh.
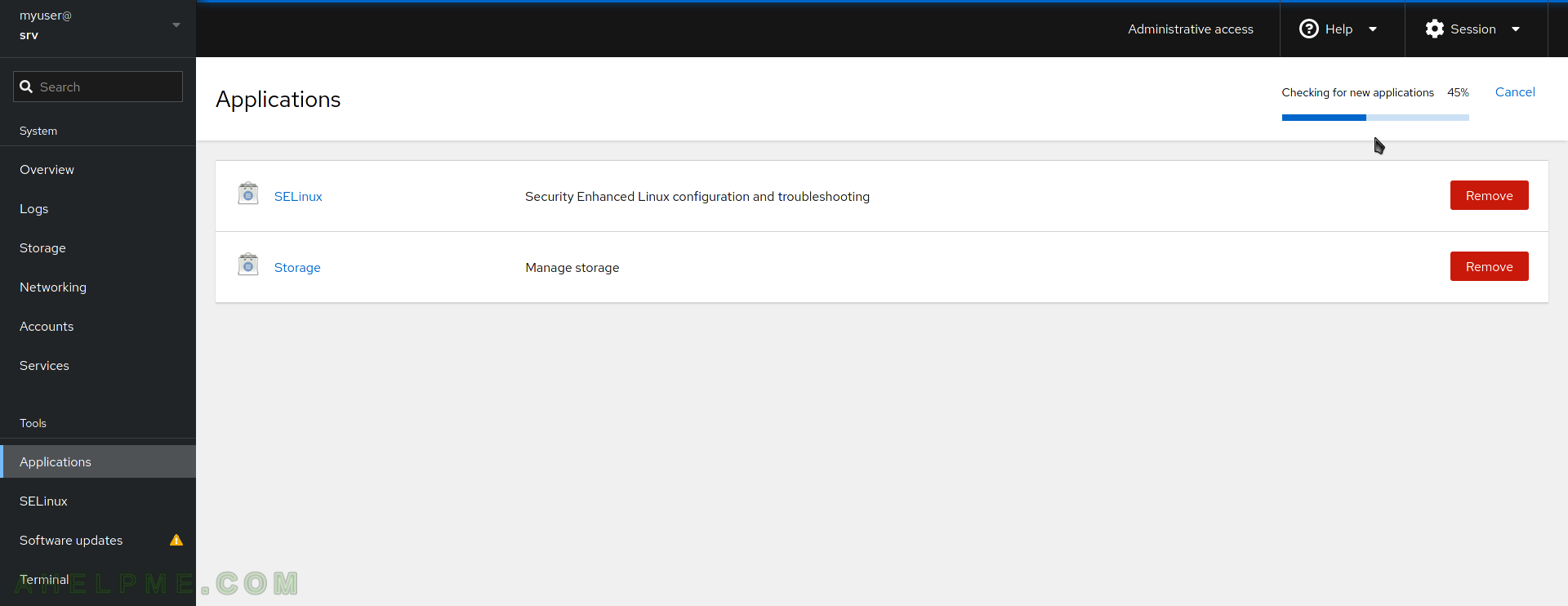
SCREENSHOT 12) In fact, Applications are the installed cockpit plugins.
The Applications extend the cockpit with new functionality and features. By default, two Applications are installed – SELinux and Storage. Currently, there are around 11 Applications such as container management podman (Red Hat’s docker), Machines, which use libvirt and QEMU to start full virtualized machines, logs, diagnostics, and more.
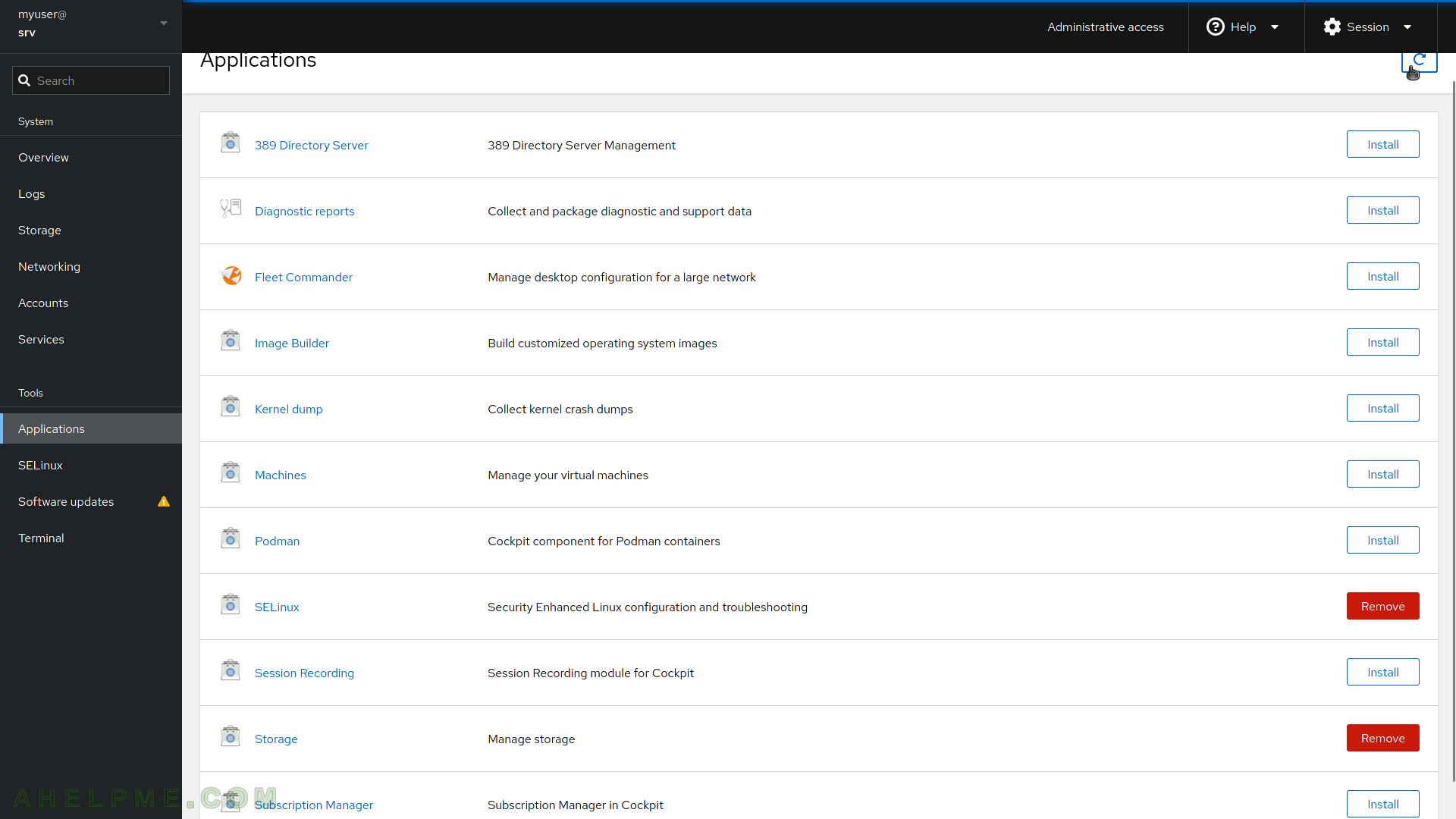
SCREENSHOT 13) SELinux application provides the ability to switch to Enforcing and Permissive modes and there is logging functionality, too.
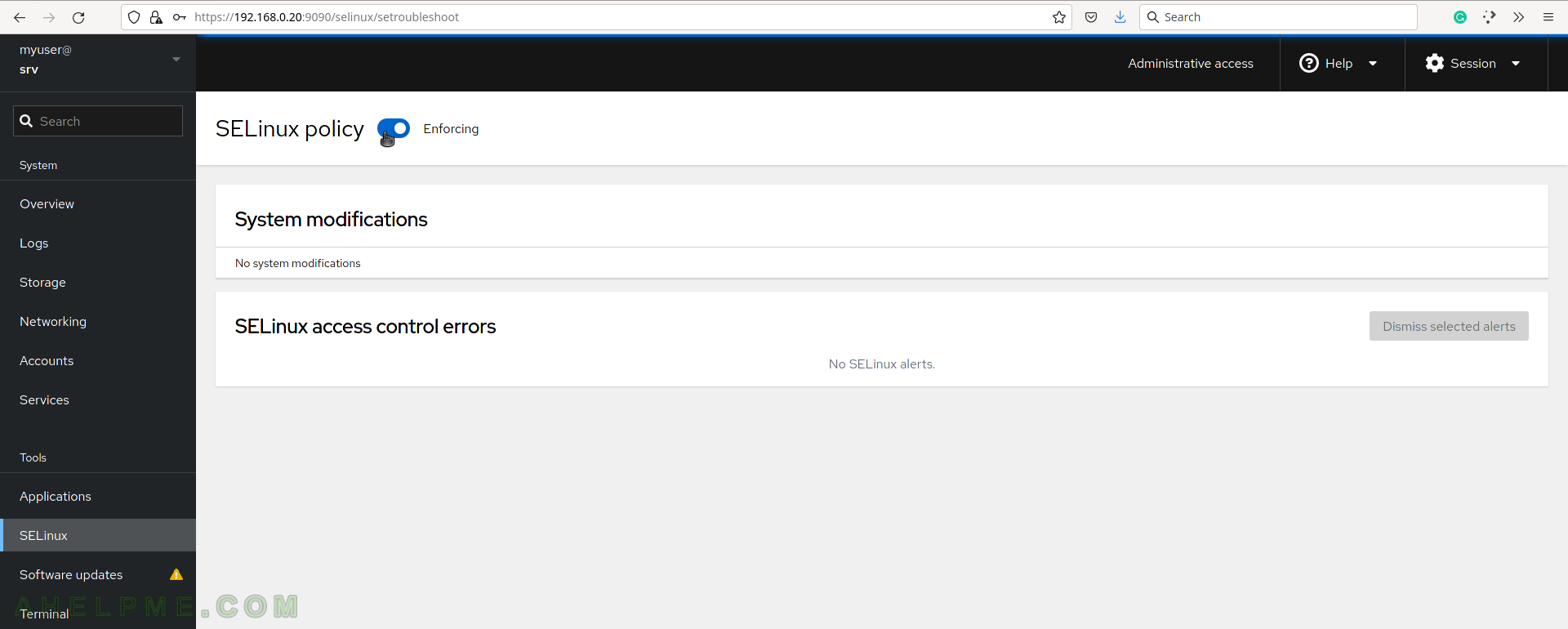
SCREENSHOT 14) The software updates page offers a detailed view of the updates and what kind of updates are pending – critical or not.
There are two main types of choices to install updates – to install only the security ones or all.
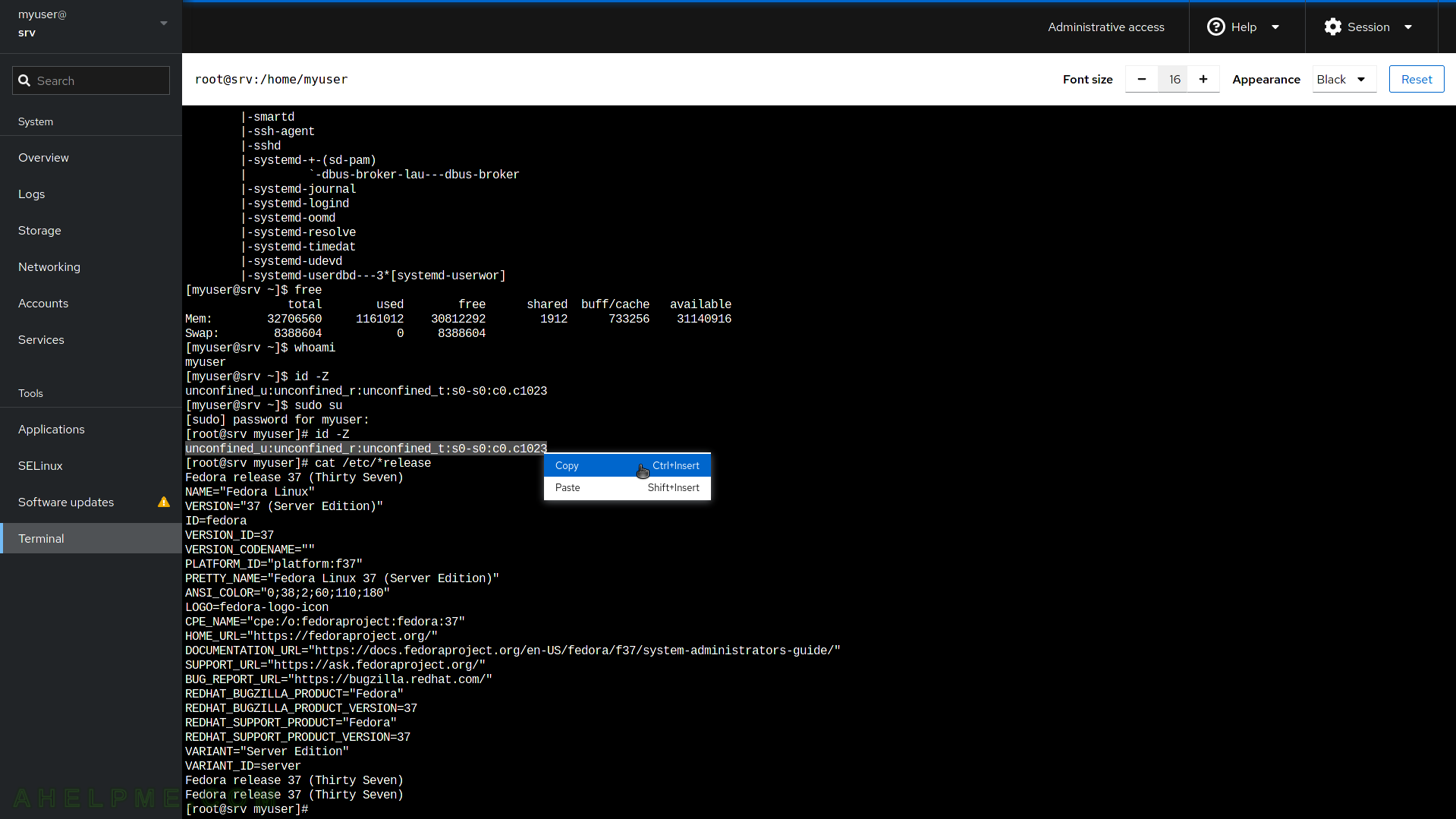
SCREENSHOT 15) There is a terminal application on the web page.
Escalating to the root user is possible. There are COPY and PASTE functionality.